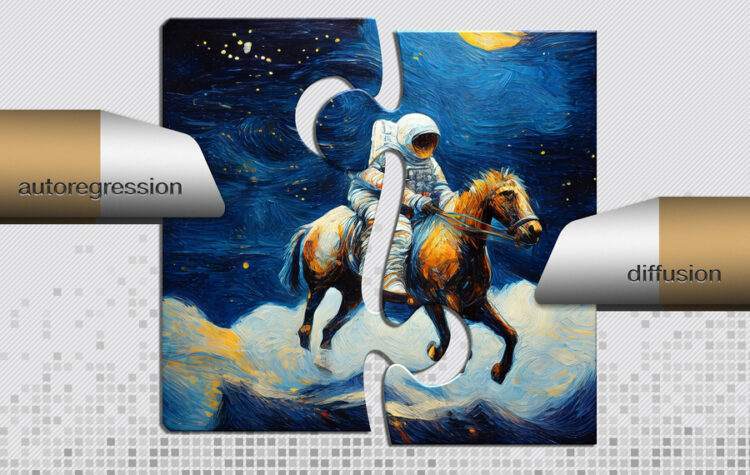

Researchers fuse the best of two popular methods to create an image generator that uses less energy and can run locally on a laptop or smartphone.
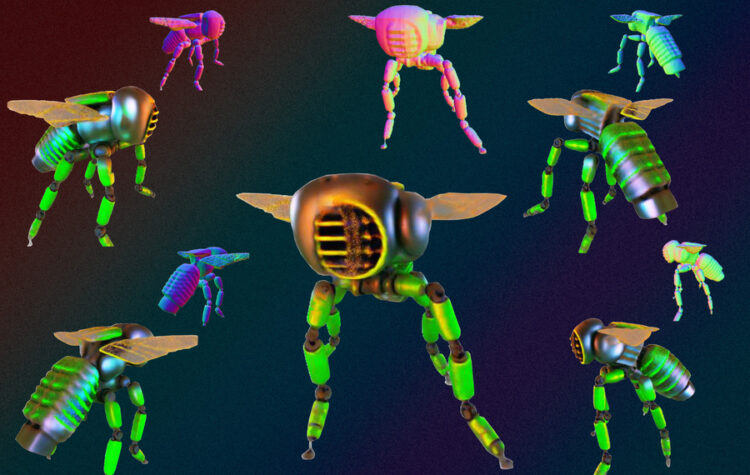

A new way to create realistic 3D shapes using generative AI
Researchers propose a simple fix to an existing technique that could help artists, designers, and engineers create better 3D models.
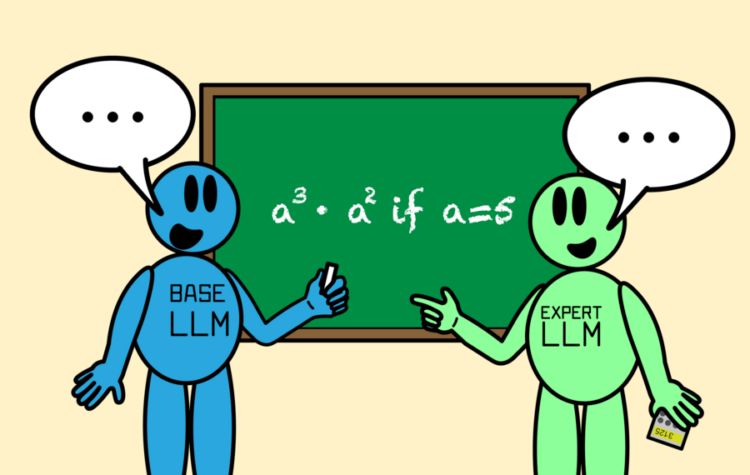
Enhancing LLM collaboration for smarter, more efficient solutions
“Co-LLM” algorithm helps a general-purpose AI model collaborate with an expert large language model by combining the best parts of both answers, leading to more factual responses.

Method prevents an AI model from being overconfident about wrong answers
More efficient than other approaches, the “Thermometer” technique could help someone know when they should trust a large language model.

Associate Professor Jonathan Ragan-Kelley optimizes how computer graphics and images are processed for the hardware of today and tomorrow.
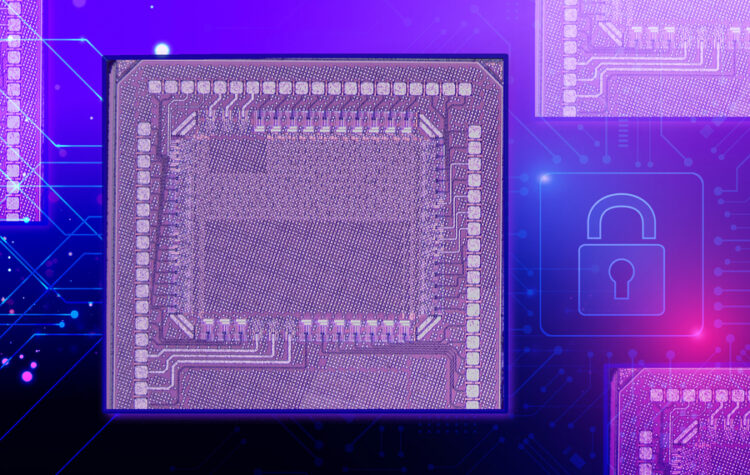
This tiny chip can safeguard user data while enabling efficient computing on a smartphone
Researchers have developed a security solution for power-hungry AI models that offers protection against two common attacks.

Caption:Anantha Chandrakasan, dean of the School of Engineering and the Vannevar Bush Professor of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, has been named as MIT’s first chief innovation and strategy officer.

Reasoning and reliability in AI
PhD students interning with the MIT-IBM Watson AI Lab look to improve natural language usage.
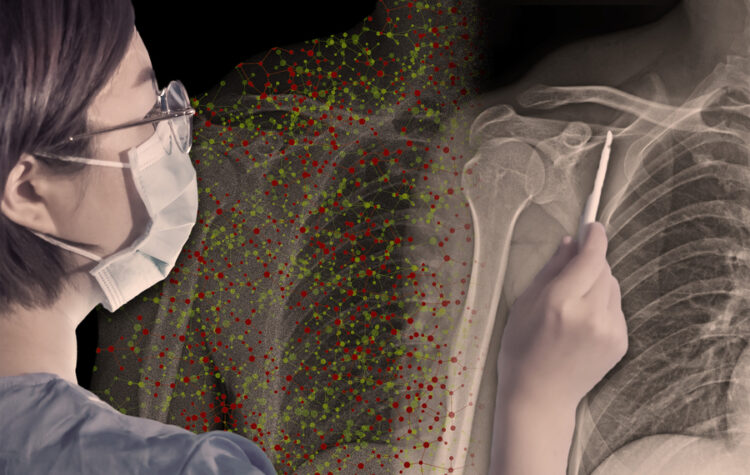
MIT researchers develop a customized onboarding process that helps a human learn when a model’s advice is trustworthy.
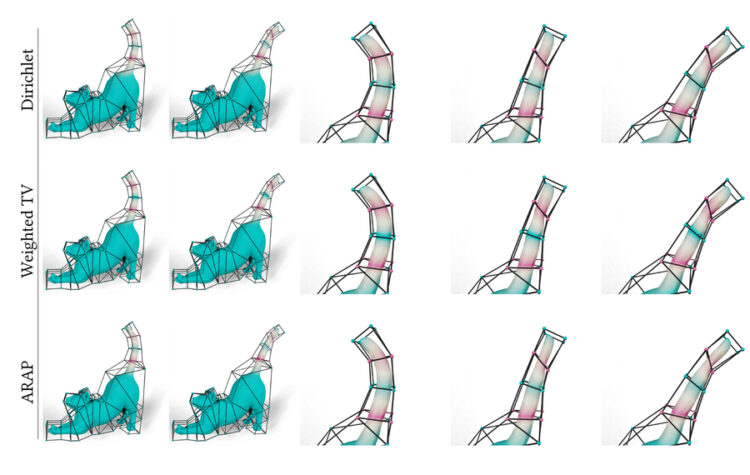
A flexible solution to help artists improve animation
This new method draws on 200-year-old geometric foundations to give artists control over the appearance of animated characters.