A blueprint for making quantum computers easier to program
A CSAIL study highlights why it is so challenging to program a quantum computer to run a quantum algorithm, and offers a conceptual model for a more user-friendly quantum computer.

A new technique can be used to predict the actions of human or AI agents who behave suboptimally while working toward unknown goals.

Department of EECS Announces 2024 Promotions
The Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science (EECS) is proud to announce multiple promotions.
How symmetry can come to the aid of machine learning
Exploiting the symmetry within datasets, MIT researchers show, can decrease the amount of data needed for training neural networks.
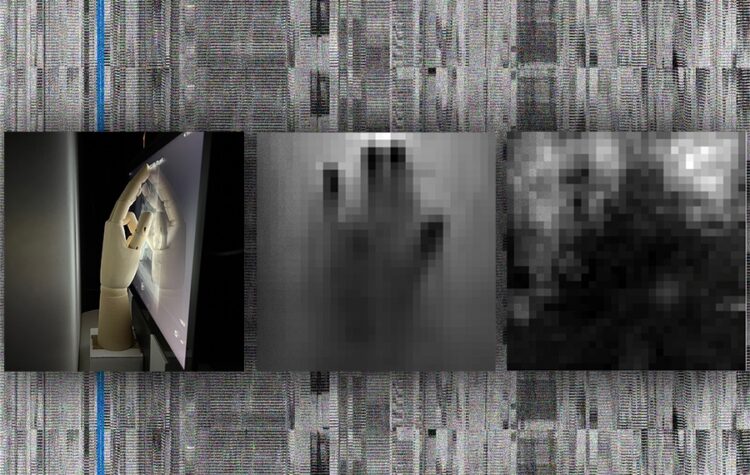

The ambient light sensors responsible for smart devices’ brightness adjustments can capture images of touch interactions like swiping and tapping for hackers.

MIT CSAIL researchers develop advanced machine-learning models that outperform current methods in detecting pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
MIT researchers develop a customized onboarding process that helps a human learn when a model’s advice is trustworthy.
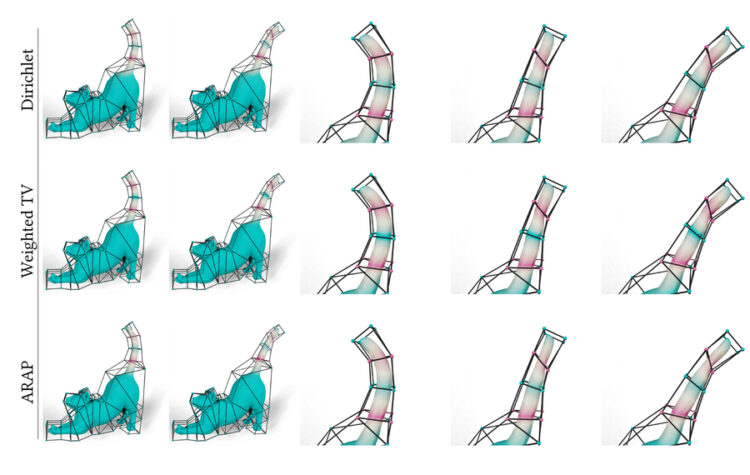
A flexible solution to help artists improve animation
This new method draws on 200-year-old geometric foundations to give artists control over the appearance of animated characters.
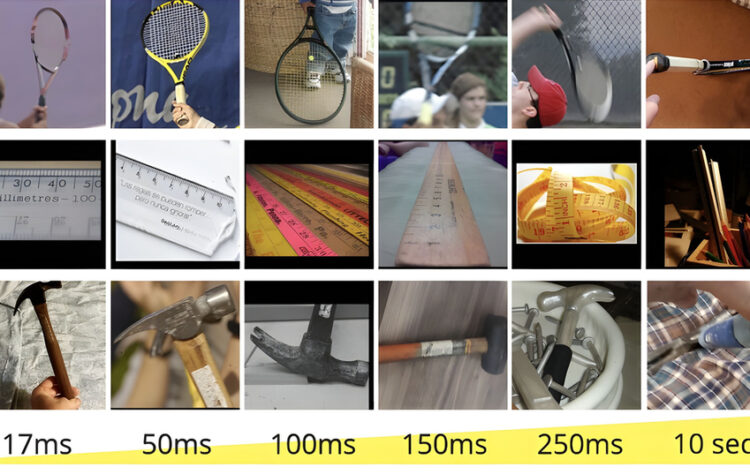
Image recognition accuracy: An unseen challenge confounding today’s AI
“Minimum viewing time” benchmark gauges image recognition complexity for AI systems by measuring the time needed for accurate human identification.

MIT’s tiny technologies go to Washington
Cancer nanomedicine was on display at the 2023 White House Demo Day.